
Network analyzers are devices used for assessing electrical network systems. They can be simply described as a signal receiver equipped with a display. All network systems aim to transmit signals with the highest efficiency and with the least distortion. Manufacturers and designers use network analysis to measure the performance of circuits and components in complex systems.
This post briefly covers the types of analyzers and the necessity of these devices in different industries.
Types of Network Analyzers
A large variety of analyzers have been developed over the years based on specific needs. For example, network analyzers detect and evaluate known signals and measure parameters like Voltage Standing Wave Ratio (VSWR), gain, isolation, loss, and group delay between two ports in multi-port networks. Spectrum analyzers mainly help users to spot unwanted signals, but they are also used to measure harmonics, false sidebands and carrier power levels among others. Vector analyzers use RF analysis with demodulation and troubleshooting abilities and are essential for manufacturing mobile handsets and base stations, and for the development process of wireless equipment.

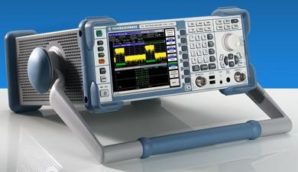
Network Analyzer [Image credit – AllenMcC, CC3.0.]
If you want well-maintained network analyzers, a vast array of analyzers is offered on rent or for secondhand purchase, from reliable test equipment rental companies, like TRS RenTelco. Equipment rental companies can help you through specifications of the analyzer best suited for you. Manufacturers also have guides, like this one from Agilent, that help you select the right analyzer for the right purpose.
The importance of early detection
How important are network analysis? Do networks need an analyzer at all, or can they do without it?
It is useful to think of networks as a complex body or structure that performs important communication and transmission tasks. Every organism or body needs maintenance and mechanisms that keeps a constant eye on what’s happening inside and to detect any issues early on, before they turn into large-scale problems.
Unlike the human body, it is certainly possible for networks to be kept under constant supervision. As part of proficient network management, it only makes sense to put your network through rigorous analysis. A network analyzer can be trusted to save your time and money by addressing each symptom before it can build up into a major crisis.
Analyzers do not just give network engineers superficial information; they can take them to the important details, pretty much like a medical scan or an X-ray examination. You will be informed of both the good and the bad events in the network and will have a comprehensive knowledge of network utilization.
Therefore, not only is there a need for regular network analysis, but there is also the need to learn to use analyzers and to stay fluent with them.
Where are analyzers needed?
Analyzers are used for many applications. Spectrum analyzers are critical in the development of electronic equipment and for approval of electronic items, including EMI and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI).
Spectrum Analyzer[Image credit –Wikipedia, CC3.0]
They find usage in military to zero-in on threats that are radio-based. Government organizations use them for tracking interference and common radio signals, like those from broadcast stations. Spectrum analyzers may also be required for temporary use, like when searching for a source of interference.
Frequency analyzers can analyze networks, transmission lines, filters and signal sources for relevant properties.
Portablility Requirements
Vector network analyzers (VNAs) can execute wide-ranging cable testing on-site, while not compromising on the quality of results. Finding problems in communications cables need portable VNAs that can help isolate and locate the fault under all sorts of environmental circumstances. Some portable VNAs can do TDR measurements to find impedance variations in cables and also perform other analyses for coaxial cables.

Portable Vector Network Analyzer [image credit – Wikipedia, CC3.0]
Other varieties of portable VNAs have in-built tracking generators that can perform transmission analysis over a long range and enable measurements on systems with long cable runs, and microwave cables, while saving time on long warm-ups and calibrations.
Vector network analyzers are also neccesary in large-scale manufacturing of mobile devices, data centers and equipment designed for commercial needs like high-speed data transfer. They can speed up the time-to-market in testing applications and reduce testing costs for fields like system integration and automotive cables among others. The need for VNAs operating across wide dynamic ranges has become prominent due to high-speed mobile networks. Base stations for such networks have very steep skirts and reject out-of-range band signals easily. VNAs can handle such problems well.
Network analyzers are essential devices in field of electronics and telecommunication. They are extremely useful in system diagnosis and maintenance of frequency and microwave devices. They are key to successful and effective maintenance of networks and will have varying applications in multiple industries.
